This guide is to help set up an automated MySQL database backup schedule for Progeny 11 on-premise installations on Windows based servers.
It uses the mysqldump program in a batch file to export all tables from a MySQL database into an .sql file. It also uses the native Windows Task Scheduler to automate running the batch file at the desired interval. Finally, there is an optional step to automatically purge older unneeded backup files and reclaim disk space, also using a batch file and the Task Scheduler.
It would be most efficient to coordinate this backup process with any existing backup process within the organization. For example, the organization might do whole server snapshots daily at midnight, so the mysqldump could be scheduled to run the hour prior.
Check the existing backup solution
- Database backup frequency
- Database archive frequency
- Database backups purge frequency
If possible, coordinate this backup process with any existing backup process within your organization. The organization might already have an enterprise backup solution in place which can archive the MySQL dumps into a central location. In this case you would want to coordinate the dump schedules with its retrieving and archiving schedule.
For example, the organization might do whole server snapshots daily at midnight, so the mysqldump could be scheduled to run the hour prior.
Add MySQL to the environment variable
Adding the MySQL bin directory to the environment variable allows you to use various MySQL client commands from the command line utility. For all supported commands, see the following webpage: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/programs-client.html
- Search for environment variable in the Windows search box, control panel, or the Windows settings.
- Click the option that appears to edit the system environment variables.
- In the System Properties window on the Advanced tab, click on the Environment Variables… button.
- In the System variables section, select the Variable with the name Path, then click the Edit… button.
- In the Edit environment variable window, click the New button.
- Enter the path to the MySQL bin directory. The default is C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin
- Click OK to save and close the Edit environment variable window.
- Click OK to close the Environment Variables window.
- Click OK to close the System Properties window.
- Now you will be able to run the mysql client tools from the command line.
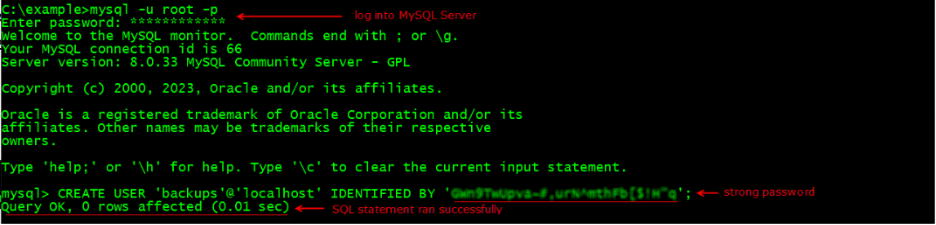
Create a MySQL database ’backups’ service account
Create a service account named backups with only the permissions needed to run the mysqldump command to create a backup.
To create the service account log into MySQL at the command prompt and run the following statements replacing password with a strong password:
- CREATE USER ‘backups’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘password’;
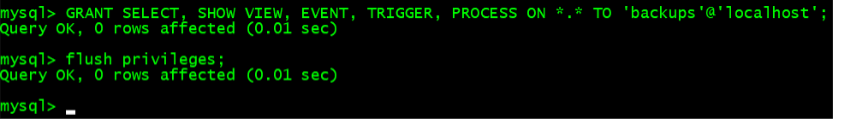
- GRANT SELECT, SHOW VIEW, EVENT, TRIGGER, PROCESS ON *.* TO ‘backups’@’localhost’;
- FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
- NOTE: The *.* in the above statements refer to DATABASE.TABLES, so if you wish for the database backups service account to run only on a specific database then replace DATABASE with that database name. You could also change the service account name to one associated with that particular database to differentiate if multiple service accounts are desired, e.g.
CREATE USER ‘research_backups‘@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘password’;
GRANT SELECT ON research.* TO ‘research_backups’@’localhost’;
etc.
Create a batch file with the mysqldump command to create a database dump
Paste the following into a text editor. Replace database with your database name, change the output path with your desired path for the database dump file, then save the file with filename mysql_backup.bat.
:: suppress command line output
@echo off
:: set date and time variables so they can be appended to the filename in YYMMDD_HHMMSS format
set datetime=%date:~4,2%%date:~7,2%%date:~12,2%_%time:~0,2%%time:~3,2%%time:~6,2%
set datetime=%datetime: =0%
:: dump the database tables to path\file
mysqldump –single-transaction –triggers –routines –events database >”C:\progeny\databases\mysql_backups\database_dump_%datetime%.sql”
:: exit the batch program
exit
:: suppress command line output
@echo off
:: set date and time variables so they can be appended to the filename in YYMMDD_HHMMSS format
set datetime=%date:~4,2%%date:~7,2%%date:~12,2%_%time:~0,2%%time:~3,2%%time:~6,2%
set datetime=%datetime: =0%
:: dump the database tables to path\file
mysqldump –single-transaction -RE -u root –pProgeny01! Databasename >”C:\progeny\databases\mysql_backups\database_dump_%datetime%.sql”
:: exit the batch program
exit
Generate a .mylogin.cnf file with an obfuscated backup user password
In this step you will generate a .mylogin.cnf file which will contain the credentials needed to run the backups.
At a command prompt type the following replacing hostname for the server’s hostname, port for your MySQL port number and backups for the backups username. You will be prompted to enter the backups user’s password:
> mysql_config_editor set -h hostname -p -P port -u backups
This will generate a mylogin.cnf file in the path C:\Users\Your User\AppData\Roaming\MySQL\.mylogin.cnf with the obfuscated credentials needed to run the mysqldump command.
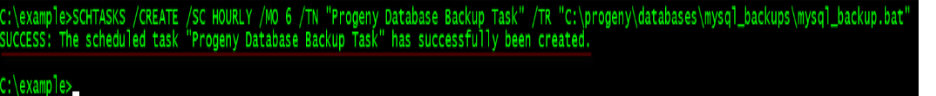
Create a task in Task Scheduler to run the batch file
In an elevated command prompt run the following command with the desired values. This example creates a task named Progeny Database Backups Task in the Progeny Backups sub-folder of Task Scheduler, which runs the mysql_backup.bat file every 6 hours. You can create multiple tasks if needed:
> SCHTASKS /CREATE /RU SYSTEM /SC HOURLY /MO 6 /TN “Progeny Backups\Progeny Database Backup Task” /TR “C:\progeny\databases\mysql_backups\mysql_backup.bat”
Command syntax:
| Parameter | Definition | Values |
| RU | Run as user | SYSTEM, NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM |
| SC | Schedule | MINUTE, HOURLY, DAILY, WEEKLY, MONTHLY |
| MO | Modifier | MINUTE: 1 – 1439 minutes HOURLY: 1 – 23 hours DAILY: 1 – 365 days WEEKLY: weeks 1 – 52 MONTHLY: 1 – 12 |
| TN | Task Name | Friendly name of the task created in the Task Library |
| TR | Task Run | Path and file name of the program to be run |
More options can be found in the Task Scheduler online help by typing SCHTASKS /CREATE /? at the command line.
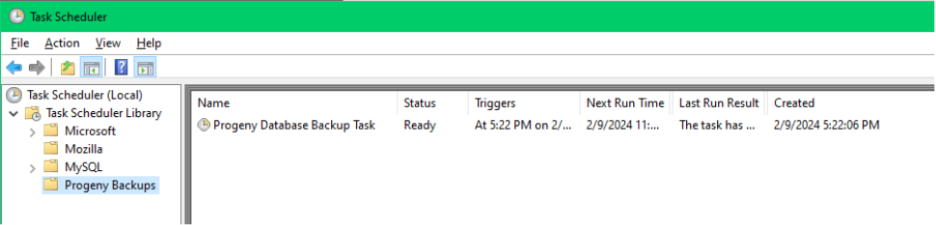
You can open the Windows Task Scheduler to confirm the task has been created and is active.
To validate that the task works as expected right click the task and select Run and confirm that a backup file has been created.
Create a batch file to periodically purge the accumulated backups
Paste the following into a text editor. This command will find all files in the path C:\progeny\databases\mysql_backups\ ending in .sql that were last modified over 90 days ago and delete them.
forfiles /P “C:\progeny\databases\mysql_backups” /M *.sql /D -90 /C ”cmd /c del /q @file”
Replace the path C:\progeny\databases\mysql_backups with the path to the folders containing your backups, and replace -90 with a last modified date less than or equal to the current date minus this number of days you would like deleted. Save the file as “C:\progeny\databases\mysql_backups\mysql_db_purge.bat” then run the following command to create a task to run this batch file weekly:
> SCHTASKS /CREATE /SC WEEKLY /TN “Progeny Backups\Progeny Database Purge Task” /TR “C:\progeny\databases\mysql_backups\mysql_db_purge.bat”